一、OGNL表达式
1.简介
OGNL:对象视图导航语言. ${user.addr.name} 这种写法就叫对象视图导航。
OGNL不仅仅可以视图导航.支持比EL表达式更加丰富的功能。
2.使用OGNL准备工作
2.1导包
struts2 的包中已经包含了.所以不需要导入额外的jar包
2.2代码准备

立即学习“Java免费学习笔记(深入)”;
@Test//准备工作public void fun1() throws Exception{//准备OGNLContext//准备RootUser rootUser = new User("tom",18);//准备ContextMap context = new HashMap();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();//将rootUser作为root部分 oc.setRoot(rootUser);//将context这个Map作为Context部分 oc.setValues(context);//书写OGNLOgnl.getValue("", oc, oc.getRoot());
} 3.基本语法演示
//取出root中user对象的name属性String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
//取出context中键为user1对象的name属性String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user2.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user2.age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
System.out.println(age);
//将root中的user对象的name属性赋值Ognl.getValue("name='jerry'", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='郝强勇',#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
//调用root中user对象的setName方法Ognl.getValue("setName('lilei')", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.setName('lucy'),#user1.getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("@cn.itheima.a_ognl.HahaUtils@echo('hello 强勇!')", oc, oc.getRoot());//Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(pi);
//创建list对象Integer size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}[0]", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.get(1)", oc, oc.getRoot()); /*System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);*///创建Map对象Integer size2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name3 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}['name']", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.get('age')", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(size2);
System.out.println(name3);
System.out.println(age);
二、OGNL与Struts2的结合
1.结合原理

ValueStack中的两部分

2.栈原理

栈是由ArrayList模拟的

栈中的两个方法的实现

访问栈中属性的特点.由上到下

3.查看值栈中两部分内容(使用DEBUG标签)
3.1Root
默认情况下,栈中放置当前访问的Action对象

PHP网络编程技术详解由浅入深,全面、系统地介绍了PHP开发技术,并提供了大量实例,供读者实战演练。另外,笔者专门为本书录制了相应的配套教学视频,以帮助读者更好地学习本书内容。这些视频和书中的实例源代码一起收录于配书光盘中。本书共分4篇。第1篇是PHP准备篇,介绍了PHP的优势、开发环境及安装;第2篇是PHP基础篇,介绍了PHP中的常量与变量、运算符与表达式、流程控制以及函数;第3篇是进阶篇,介绍

3.2Context


Context部分就是ActionContext数据中心
4.struts2与ognl结合体现
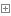
4.1参数接收


如何获得值栈对象,值栈对象与ActionContext对象是互相引用的
//压入栈顶//1获得值栈ValueStack vs = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();//2将u压入栈顶vs.push(u);
4.2配置文件中
Demo1Action/${name}
5.扩展:request对象的getAttribute方法
查找顺序:

三、练习:客户列表
public String list() throws Exception {//1 接受参数String cust_name = ServletActionContext.getRequest().getParameter("cust_name");//2 创建离线查询对象DetachedCriteria dc =DetachedCriteria.forClass(Customer.class);//3 判断参数拼装条件if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(cust_name)){
dc.add(Restrictions.like("cust_name", "%"+cust_name+"%"));
}//4 调用Service将离线对象传递List list = cs.getAll(dc);//5 将返回的list放入request域.转发到list.jsp显示 //ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("list", list);// 放到ActionContextActionContext.getContext().put("list", list); return "list";
} 注意: